Finding the Right Rehab for Your Teen or Young Adult



Kayla holds nearly a decade of experience in the rehab space, including in-house content management at a leading treatment center and founding a rehab-specialized content agency. She believes addiction and mental health issues are universal human experiences that can serve as important entry points onto a path toward self-realization and well-being.




Kayla holds nearly a decade of experience in the rehab space, including in-house content management at a leading treatment center and founding a rehab-specialized content agency. She believes addiction and mental health issues are universal human experiences that can serve as important entry points onto a path toward self-realization and well-being.
Anyone can struggle with substance use. Whatever your age, gender, job, or relationship status, you deserve to get the care you need. However, it can sometimes be hard to know what interventions would be most helpful. This is especially true for teens with substance use disorders.
Substance use during adolescence may have long-term effects on brain chemistry.1 For example, “cocaine exposure during adolescence may lead to miswiring in the developing brain and result in long-lasting behavioral problems, such as increased risk-taking, in adulthood.” Because of this, it’s especially important to get teens the help they need in order to begin recovery.
Young people may not always be able to recognize that they need help. And even when they do, they may not be legally or financially capable of seeking that help on their own. Whether you’re a teen or an adult caring for a teen with substance use disorder, the good news is that (specialized) treatment is widely available. Many rehabs offer programs created specifically for younger clients.
If you’re considering rehab for your teen, it’s important to understand the different options available. Depending on the client’s age and geographical location, there may be certain types of treatment that are more appropriate. This decision will also be influenced by your teen’s unique history, diagnoses, and treatment goals.
Reasons for Teen Substance Use
Research suggests that “the human brain is still maturing during the adolescent years.2 The developing brain may help explain why adolescents sometimes make decisions that are risky and can lead to safety or health concerns, including unique vulnerabilities to drug abuse.”
Beyond the simple fact of their age, there are many elements that impact a young person’s likelihood to misuse substances. Among them are risk factors, which make substance use more likely, and protective factors, which guard against these behaviors.
These external influences change with a person’s age. While that’s true for all clients, these changes occur more drastically in children, adolescents, and young adults. For example, middle school students who are too harshly disciplined are at greater risk for substance use disorders. Receiving support from extended family, on the other hand, makes substance abuse less likely in this population. Slightly older adolescents are at greater risk for substance misuse when they lack adult supervision, and at lower risk when family members set clear expectations.3
Also, teens are experiencing heightened stress in this turbulent era of history.4 According to one study, even teens who had not experienced early life stress—such as neglect or abuse—were prone to “increases in anxiety and depression symptoms” during 2020. In this context, young people may be at a greater risk of developing mental health conditions than they once were.
It’s impossible to guard against every single circumstance that increases the risk of teen substance misuse. However, it can be helpful to familiarize yourself with some of the most prevalent risk factors. Whether or not you’re able to protect yourself or your teen from these stressors, knowing what they are may empower you to get help when it’s needed.
Parental Substance Use
If an adolescent is close to an adult who has a substance use disorder, they may be at a higher risk for developing one themselves.5 For some young people, this is simply a way of enacting the same behavior they’ve seen modeled. Others may use substances in order to cope with the stress of an unstable home life.
Strained familial relationships, financial insecurity, and similar issues can be hugely impactful. However, instability refers to more than these external circumstances. These teens may also have genetic predispositions to substance use disorders, as well as other mental health diagnoses.
Co-Occurring Disorders
Certain mental health concerns, such as depression and ADHD, make teens and young adults more likely to misuse substances.6 In some cases, this is an attempt to self-medicate. However, it’s not always that simple.
For teens with multiple diagnoses, the root cause of substance use can easily become a question of the chicken or the egg. As their brain chemistry continues to change, due to either normal development or unhealthy habits, they may begin to develop co-occurring disorders that make substance use even more appealing.
Whatever the cause of this behavior, few teens have the resources to pull out of this cycle without external interventions. In some cases, inpatient treatment is the most effective way to begin recovery.
Choosing a Rehab for a Young Adult
If you’re a parent or guardian supporting a struggling teenager, it can be difficult to know what’s best for them. And even if you’re confident that they should go to rehab, you may or may not be legally allowed to make that decision on their behalf
In some U.S. states, a parent can unilaterally decide to send a teen to rehab. In other areas, minors’ consent is also required. This varies widely based on the client’s exact age and geographical location. It’s best to learn what your family’s options are before making any specific plans regarding residential treatment.
The client’s age will also help determine which treatment program is best for them. For example, while it may seem that children and younger teens are more likely to grow out of a difficult phase, they may actually be in greater need of interventions. According to one study, “people are most likely to begin abusing drugs during adolescence, and the longer adolescents defer experimentation, the less likely they are to develop long-term drug abuse problems.”7
Many rehabs often treat a wide variety of mental health concerns, not limited to substance use disorders. Teens and young adults may also benefit from rehab if they’re struggling with eating disorders, personality disorders, or even PTSD. Each of these diagnoses requires a slightly different approach to treatment, possibly including different levels of family involvement.
Some teens are able to live at home during treatment, receiving in-person support from family and friends while they begin recovery. Others may benefit from traveling to rehab. This gives clients both physical and emotional space from the challenges of daily life. It can also teach young people to set boundaries with those who enable their substance use. While this change of scenery may seem drastic, it has the potential to be extremely helpful. Remember that there is no one right way to heal; just the right way for each individual person.
Types of Teen Rehab Programs
If and when you’re ready to choose a rehab center, it’s best to learn as much as possible about the available options. Various programs specialize in treating different conditions, and each takes a unique approach to the process of healing. Because of this, it’s best to choose a facility that is qualified to meet your teen’s unique needs.
Substance Use and Eating Disorders
Eating disorders are extremely common among adolescents. As of 2018, as many as 10% of young women suffered from an eating disorder.8 What’s more, a growing body of research links eating disorders with addiction.9 One theory even suggests that anorexia nervosa is in fact “an addiction to the body’s endogenous opioids.” A number of rehabs focus on helping clients with one or both of these diagnoses.
Gender-Specific Treatment
For some clients, having space from people of different genders can feel like a much-needed break. This gender-specific approach to recovery may be especially helpful for adolescents. Studies show that young men and women exhibit “unique patterns of substance use,”10 and may therefore benefit from distinct approaches to treatment.
Some rehabs focus on treating young women. The program at Foothills at Red Oak Recovery, on the other hand, is tailored to meet the needs of young men, as well as non-binary and gender non-conforming teens. Although it is an LGBTQ+-affirming rehab, it is probably not the right fit for cis women.
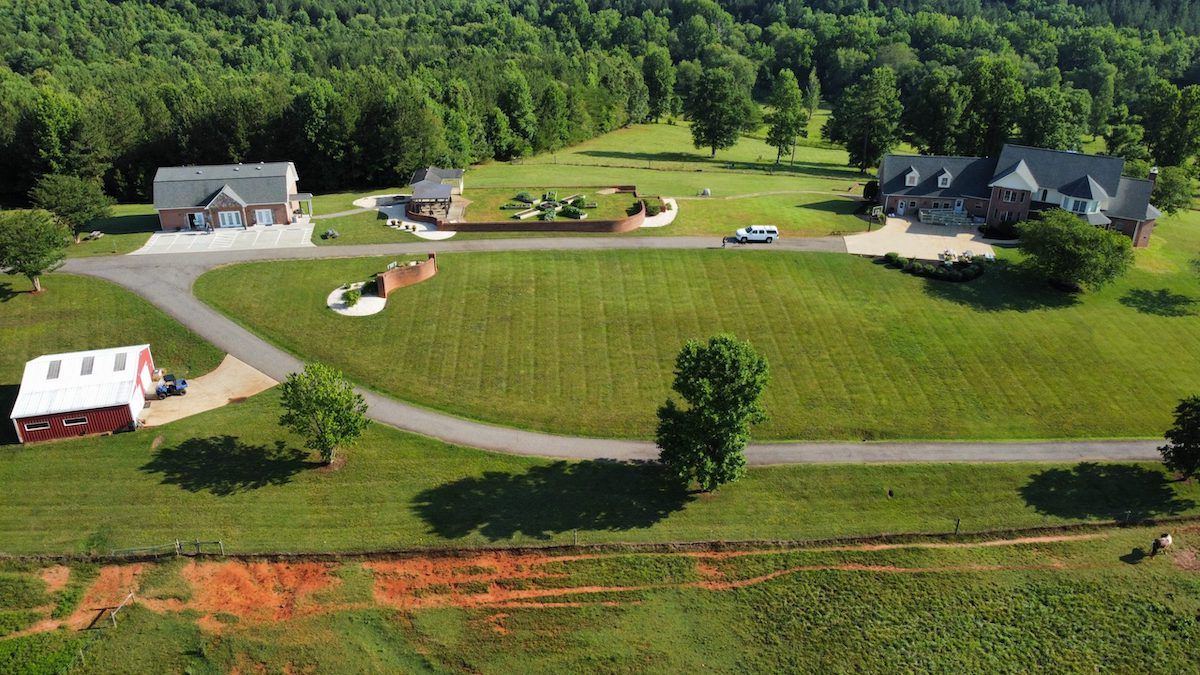

Foothills at Red Oak in Ellenboro, North Carolina has specialized programs for young men, non-binary and gender non-conforming teens.
In this protected environment, clients are invited to explore their developing identities. According to staff, “Adolescence is a time of self-discovery and identity formation…If one successfully navigates the tasks during this stage of life, one emerges with a solid sense of identity. This is a sense of knowing oneself despite the chaos and pressures of the world around them and is paramount to making healthy, value-based decisions.”
Experiential Therapy
Experiential therapy can be hugely beneficial for people of all ages. In this group of modalities, you may go skiing, river rafting, or rock climbing. Some rehabs even take their clients on adventure outings, where they might hike the lip of a volcano or swim with the dolphins.
These experiences aren’t just fun excursions; they’re also ways to practice the skills learned in talk therapy in a different context. They can also encourage clients to develop new hobbies, and help to restore the connection between mind and body. The latter is especially important for teens in recovery.
By surfing, horseback riding, or just playing sports, young people can get back in touch with their bodies and learn how it feels to be physically healthy. Experts theorize that this has a lasting impact on their continued sobriety and health. According to one study, “continued physical health for rehabilitated adolescent drug addicts is crucial…since it could enhance the effectiveness of rehabilitation.”11
With this in mind, some adolescent rehab programs have a special focus on physical activity. Pacific Quest, for example, is a wilderness therapy program located on Hawaii’s Big Island. Here, clients participate in outdoor programming which may include hiking, paddle boarding, swimming, sailing, and more. Participants also perform community service during their time in residence. Through this process, they are encouraged to learn how to engage with nature, their communities, and themselves in a healthy way.
Personalized Treatment
There are numerous ways to approach recovery. Although many teens benefit from highly structured rehab programs, others may require a more nuanced approach. For these clients, personalized treatment may be the best option.
Pacific Teen Treatment, for example, treats only six clients at a time. Each teen is assigned a primary, secondary, and family therapist. Their team of providers works together to carry out a highly individualized plan of care. This approach may not be appropriate for all clients—especially those who want to focus on improving their interpersonal dynamics within a larger cohort. But it can be extremely effective for families who are committed to healing their relationships with one another.
Family Therapy
Adolescent substance misuse impacts family dynamics.12 According to one group of experts, “every chemically dependent person has a significant impact on the lives of several other people.” Because of this, it’s important for the parents, siblings, and other relatives of these clients to engage in their own healing processes.
In many cases, family therapy is a productive way to approach this. Most adolescent rehab programs offer some version of family therapy. This may include in-person sessions, video chats, or regularly scheduled phone calls.
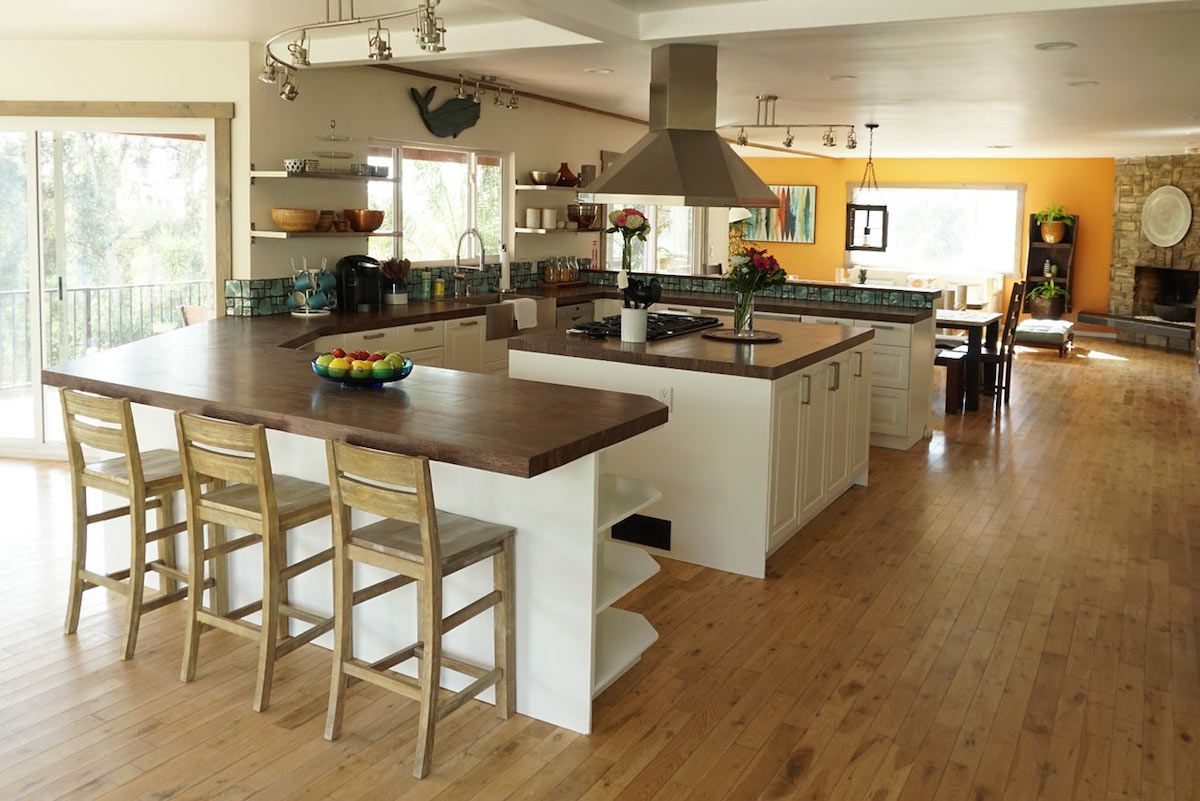

A peek inside the calming environment at Pacific Teen Treatment in Malibu, California, where family therapy is a key area of focus.
Some facilities may limit clients’ communication with people outside of their cohort. Often, these programs restrict cell phone use during rehab. Others may prohibit calls or visits at the beginning of the program, but encourage this type of contact after some time has passed. Every rehab has its own unique guidelines, and those guidelines may vary from one client to another.
Therapy isn’t easy. This process may bring up traumatic memories and shine a light on difficult family dynamics. Even so, it is often an essential component of helping a teen recover from substance misuse.
Growing Beyond Substance Use
Substance use disorders are serious conditions. At any age, and especially for teenagers, this behavior should not be dismissed as “just a phase.” That being said, it can be temporary. It’s always possible to heal and grow beyond unhealthy habits.
A person’s adolescent years are powerfully creative. Over time, teens will inevitably learn more about themselves, defining their identities and discovering their own needs, goals, and values. It’s extremely important to connect these clients with the help they need and deserve. It’s also important to trust the process.
To see reviews, virtually tour facilities, and more, see our curated list of adolescent rehab programs.
FAQs
-
Cocaine’s effects on the teenage brain. Vanderbilt University. https://news.vanderbilt.edu/2011/06/24/cocaines-teenage-brain/
-
Winters, K. C., & Arria, A. (2011). Adolescent brain development and drugs. The Prevention Researcher, 18(2), 21-24. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3399589/
-
Risk and protective factors | youth. Gov. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://youth.gov/youth-topics/substance-use/risk-and-protective-factors . https://youth.gov/youth-topics/risk-and-protective-factors
-
Cohen, Z. P., Cosgrove, K. T., DeVille, D. C., Akeman, E., Singh, M. K., White, E., Stewart, J. L., Aupperle, R. L., Paulus, M. P., & Kirlic, N. (2021). The impact of covid-19 on adolescent mental health: Preliminary findings from a longitudinal sample of healthy and at-risk adolescents. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 9, 440. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.622608
-
Whitesell, M., Bachand, A., Peel, J., & Brown, M. (2013). Familial, social, and individual factors contributing to risk for adolescent substance use. Journal of Addiction, 2013, 579310. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/579310
-
Gau, S. S. F., Chong, M.-Y., Yang, P., Yen, C.-F., Liang, K.-Y., & Cheng, A. T. A. (2007). Psychiatric and psychosocial predictors of substance use disorders among adolescents: Longitudinal study. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 190(1), 42–48. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.106.022871
-
Garofoli, M. (2020). Adolescent substance abuse. Primary Care, 47(2), 383–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2020.02.013
-
Eating disorders in teens. (n.d.). Retrieved November 3, 2021, from https://www.aacap.org/AACAP/Families_and_Youth/Facts_for_Families/FFF-Guide/Teenagers-With-Eating-Disorders-002.aspx
-
Davis, C., & Claridge, G. (1998). The eating disorders as addiction: A psychobiological perspective. Addictive Behaviors, 23(4), 463–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4603(98)00009-4
-
Picoito, J., Santos, C., Loureiro, I., Aguiar, P., & Nunes, C. (2019). Gender-specific substance use patterns and associations with individual, family, peer, and school factors in 15-year-old Portuguese adolescents: A latent class regression analysis. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health, 13, 21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-019-0281-4
-
Latief, M. I., & Solli, A. (2020). Social challenges of teen in recovery from drugs addictions: A case study of Makassar, Indonesia. Enfermería Clínica, 30, 390–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enfcli.2019.11.005
-
Semlitz, L., & Gold, M. S. (1986). Adolescent drug abuse. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. The Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 9(3), 455–473. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK37585/
Our Promise
How Is Recovery.com Different?
We believe everyone deserves access to accurate, unbiased information about mental health and recovery. That’s why we have a comprehensive set of treatment providers and don't charge for inclusion. Any center that meets our criteria can list for free. We do not and have never accepted fees for referring someone to a particular center. Providers who advertise with us must be verified by our Research Team and we clearly mark their status as advertisers.
Our goal is to help you choose the best path for your recovery. That begins with information you can trust.